Android SQLite Tutorial
SQLite is an open-source relational database i.e. used to perform database operations on android devices such as storing, manipulating or retrieving persistent data from the database.
It is embedded in android bydefault. So, there is no need to perform any database setup or administration task.
Here, we are going to see the example of sqlite to store and fetch the data. Data is displayed in the logcat. For displaying data on the spinner or listview, move to the next page.
SQLiteOpenHelper class provides the functionality to use the SQLite database.
SQLiteOpenHelper class
The android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper class is used for database creation and version management. For performing any database operation, you have to provide the implementation of onCreate() and onUpgrade() methods of SQLiteOpenHelper class.
Constructors of SQLiteOpenHelper class
There are two constructors of SQLiteOpenHelper class.
| Constructor | Description |
|---|
| SQLiteOpenHelper(Context context, String name, SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory factory, int version) | creates an object for creating, opening and managing the database. |
| SQLiteOpenHelper(Context context, String name, SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory factory, int version, DatabaseErrorHandler errorHandler) | creates an object for creating, opening and managing the database. It specifies the error handler. |
Methods of SQLiteOpenHelper class
There are many methods in SQLiteOpenHelper class. Some of them are as follows:
| Method | Description |
|---|
| public abstract void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) | called only once when database is created for the first time. |
| public abstract void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) | called when database needs to be upgraded. |
| public synchronized void close () | closes the database object. |
| public void onDowngrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) | called when database needs to be downgraded. |
SQLiteDatabase class
It contains methods to be performed on sqlite database such as create, update, delete, select etc.
Methods of SQLiteDatabase class
There are many methods in SQLiteDatabase class. Some of them are as follows:
| Method | Description |
|---|
| void execSQL(String sql) | executes the sql query not select query. |
| long insert(String table, String nullColumnHack, ContentValues values) | inserts a record on the database. The table specifies the table name, nullColumnHack doesn't allow completely null values. If second argument is null, android will store null values if values are empty. The third argument specifies the values to be stored. |
| int update(String table, ContentValues values, String whereClause, String[] whereArgs) | updates a row. |
| Cursor query(String table, String[] columns, String selection, String[] selectionArgs, String groupBy, String having, String orderBy) | returns a cursor over the resultset. |
Example of android SQLite database
Let's see the simple example of android sqlite database.
File: Contact.java
- package example.javatpoint.com.sqlitetutorial;
-
- public class Contact {
- int _id;
- String _name;
- String _phone_number;
- public Contact(){ }
- public Contact(int id, String name, String _phone_number){
- this._id = id;
- this._name = name;
- this._phone_number = _phone_number;
- }
-
- public Contact(String name, String _phone_number){
- this._name = name;
- this._phone_number = _phone_number;
- }
- public int getID(){
- return this._id;
- }
-
- public void setID(int id){
- this._id = id;
- }
-
- public String getName(){
- return this._name;
- }
-
- public void setName(String name){
- this._name = name;
- }
-
- public String getPhoneNumber(){
- return this._phone_number;
- }
-
- public void setPhoneNumber(String phone_number){
- this._phone_number = phone_number;
- }
- }
File: DatabaseHandler.java
Now, let's create the database handler class that extends SQLiteOpenHelper class and provides the implementation of its methods.
- package example.javatpoint.com.sqlitetutorial;
-
- import android.content.ContentValues;
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.database.Cursor;
- import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
- import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.List;
-
-
- public class DatabaseHandler extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
- private static final int DATABASE_VERSION = 1;
- private static final String DATABASE_NAME = "contactsManager";
- private static final String TABLE_CONTACTS = "contacts";
- private static final String KEY_ID = "id";
- private static final String KEY_NAME = "name";
- private static final String KEY_PH_NO = "phone_number";
-
- public DatabaseHandler(Context context) {
- super(context, DATABASE_NAME, null, DATABASE_VERSION);
-
- }
-
-
- @Override
- public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
- String CREATE_CONTACTS_TABLE = "CREATE TABLE " + TABLE_CONTACTS + "("
- + KEY_ID + " INTEGER PRIMARY KEY," + KEY_NAME + " TEXT,"
- + KEY_PH_NO + " TEXT" + ")";
- db.execSQL(CREATE_CONTACTS_TABLE);
- }
-
-
- @Override
- public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
-
- db.execSQL("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS " + TABLE_CONTACTS);
-
-
- onCreate(db);
- }
-
-
- void addContact(Contact contact) {
- SQLiteDatabase db = this.getWritableDatabase();
-
- ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
- values.put(KEY_NAME, contact.getName());
- values.put(KEY_PH_NO, contact.getPhoneNumber());
-
-
- db.insert(TABLE_CONTACTS, null, values);
-
- db.close();
- }
-
-
- Contact getContact(int id) {
- SQLiteDatabase db = this.getReadableDatabase();
-
- Cursor cursor = db.query(TABLE_CONTACTS, new String[] { KEY_ID,
- KEY_NAME, KEY_PH_NO }, KEY_ID + "=?",
- new String[] { String.valueOf(id) }, null, null, null, null);
- if (cursor != null)
- cursor.moveToFirst();
-
- Contact contact = new Contact(Integer.parseInt(cursor.getString(0)),
- cursor.getString(1), cursor.getString(2));
-
- return contact;
- }
-
-
- public List<Contact> getAllContacts() {
- List<Contact> contactList = new ArrayList<Contact>();
-
- String selectQuery = "SELECT * FROM " + TABLE_CONTACTS;
-
- SQLiteDatabase db = this.getWritableDatabase();
- Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery(selectQuery, null);
-
-
- if (cursor.moveToFirst()) {
- do {
- Contact contact = new Contact();
- contact.setID(Integer.parseInt(cursor.getString(0)));
- contact.setName(cursor.getString(1));
- contact.setPhoneNumber(cursor.getString(2));
-
- contactList.add(contact);
- } while (cursor.moveToNext());
- }
-
-
- return contactList;
- }
-
-
- public int updateContact(Contact contact) {
- SQLiteDatabase db = this.getWritableDatabase();
-
- ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
- values.put(KEY_NAME, contact.getName());
- values.put(KEY_PH_NO, contact.getPhoneNumber());
-
-
- return db.update(TABLE_CONTACTS, values, KEY_ID + " = ?",
- new String[] { String.valueOf(contact.getID()) });
- }
-
-
- public void deleteContact(Contact contact) {
- SQLiteDatabase db = this.getWritableDatabase();
- db.delete(TABLE_CONTACTS, KEY_ID + " = ?",
- new String[] { String.valueOf(contact.getID()) });
- db.close();
- }
-
-
- public int getContactsCount() {
- String countQuery = "SELECT * FROM " + TABLE_CONTACTS;
- SQLiteDatabase db = this.getReadableDatabase();
- Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery(countQuery, null);
- cursor.close();
-
-
- return cursor.getCount();
- }
-
- }
File: MainActivity.java
- package example.javatpoint.com.sqlitetutorial;
-
- import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.util.Log;
- import java.util.List;
-
- public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
-
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
- DatabaseHandler db = new DatabaseHandler(this);
-
-
- Log.d("Insert: ", "Inserting ..");
- db.addContact(new Contact("Ravi", "9100000000"));
- db.addContact(new Contact("Srinivas", "9199999999"));
- db.addContact(new Contact("Tommy", "9522222222"));
- db.addContact(new Contact("Karthik", "9533333333"));
-
-
- Log.d("Reading: ", "Reading all contacts..");
- List<Contact> contacts = db.getAllContacts();
-
- for (Contact cn : contacts) {
- String log = "Id: " + cn.getID() + " ,Name: " + cn.getName() + " ,Phone: " +
- cn.getPhoneNumber();
-
- Log.d("Name: ", log);
- }
- }
- }
Output:
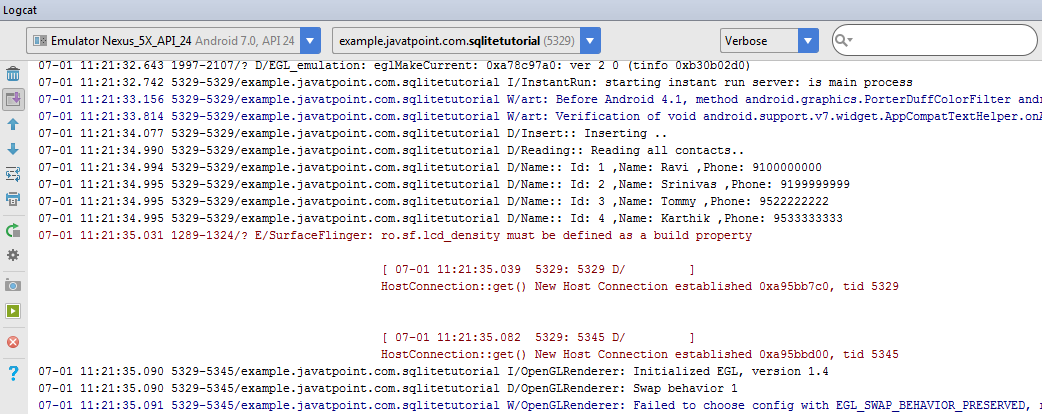
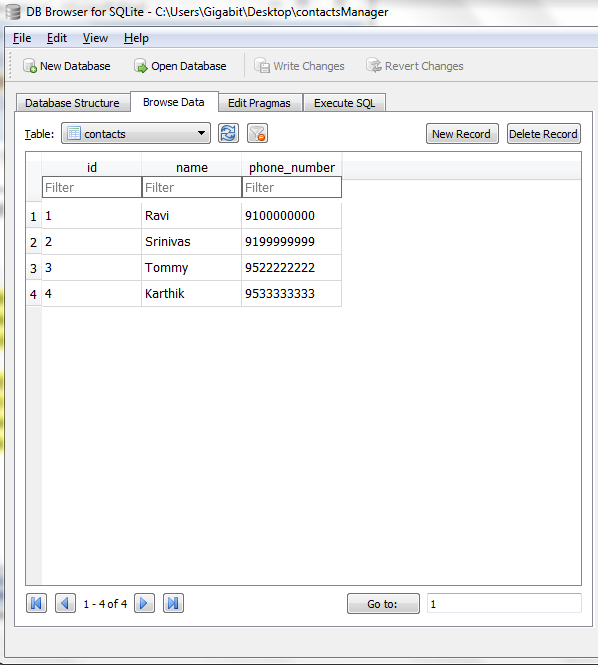
How to view the data stored in sqlite in android studio?
Follow the following steps to view the database and its data stored in android sqlite:
- Open File Explorer.
- Go to data directory inside data directory.
- Search for your application package name.
- Inside your application package go to databases where you will found your database (contactsManager).
- Save your database (contactsManager) anywhere you like.
- Download any SqLite browser plugins or tool (in my case DB Browser for SQLite).
- Launch DB Browser for SQLite and open your database (contactsManager).
- Go to Browse Data -> select your table (contacts) you will see the data stored.


No comments:
Post a Comment